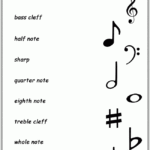
Printable Music Theory Worksheets For Beginners – Sheet music refers to the handwritten or printed form of musical notation. It makes use of musical symbols to identify the rhythms, notes, or chords of an arrangement. The majority of sheet music is printed on paper. It’s an excellent source for musicians and an extremely popular method for those to learn how to play instruments.
There are a variety of types of printed music. It’s ideal for all students. These materials are hand-crafted by independent artists. The artists are backed with each purchase. To create a learning environment that is enjoyable for your children, make use of printable music.
The first printed music was not accessible for download. Numerous publishers began to sell sheet music printed for promotional purposes. The early publications were comprised of catalogs of songs, lists and tunes. Later, publishers started to print whole pages of music. Some companies even created sheet music to advertise their products. To avoid violating the conditions of these licenses the publishers were required to provide credit.
The first printed music book was called the Mainz Psalter. Baroque composers used moveable font to mix musical markings and notes. Many composers made use of the figured bass in this time. Luckily, the printing press made these techniques possible. You can find the print version of this piece in many libraries.
Although printing a music sheet can be simple but there are some important things to keep in mind. First, you must get the correct print license. A print license usually is between 3 and 5 year. The agreement allows for inventory that is in a state of non-use to be sold for sixto twelve months. Music publishers will likely charge an amount for this use. After that, you must decide on how the printed sheets of music should be distributed.
Before the invention of the printing press, it was difficult to print music. It took several centuries before printing was a widespread procedure. The method of using moving type for printing music was a challenge until the invention of printing presses helped make the process simpler. Petrucci was able to overcome this issue by inventing the triple-impression method, which included printing staff lines, words, and notes in three separate impressions. This method was later used for the printed music that we currently use.
Printing music made it easier for amateurs and professional musicians to access music. This also made it simpler for amateur musicians to create music. It was also good news for the industry of music as composers were able to create more music to be performed by amateur musicians. This resulted in secular music growing in popularity.
Before purchasing sheet music for music it is important to know some things to keep in mind. The first is that the notes in a performance score or part should be easy to read. This is due to the fact that they should be able to be read using a music stand. A binding style is also essential. It can be difficult for a musician to keep a piece of music open with a musical stand when the binding is too thick. So, it’s best to buy a paper sheet which will lay flat on the stand.
The tempo is also an important aspect to consider when choosing music scores. The composer may need the performer to repeat a particular section of music, based on the piece. In the music sheet, composers could declare that the repetition is performed to convey this message to the listeners. The repeat sign is represented by two dots on the end of a section. The repeat sign may be used to cover the entire length of a bar or just one bar. There are various kinds.
Partbooks were common during the Renaissance period to create multi-part polyphonic pieces of music. For a madrigal with multiple parts, for example, the parts would each be published in a separate book. Partbooks could be used both by instrumentalists and singers. Multi-part scores were not printed during this period. Josquin des Prez, however, is acknowledged for making use of the score format.
A short score is another typical form. It’s the shortened version of a full score. This is the norm for orchestral music and may be utilized as a work copy for composers. While shorter scores aren’t often released, they are often used in rehearsals and for studies.