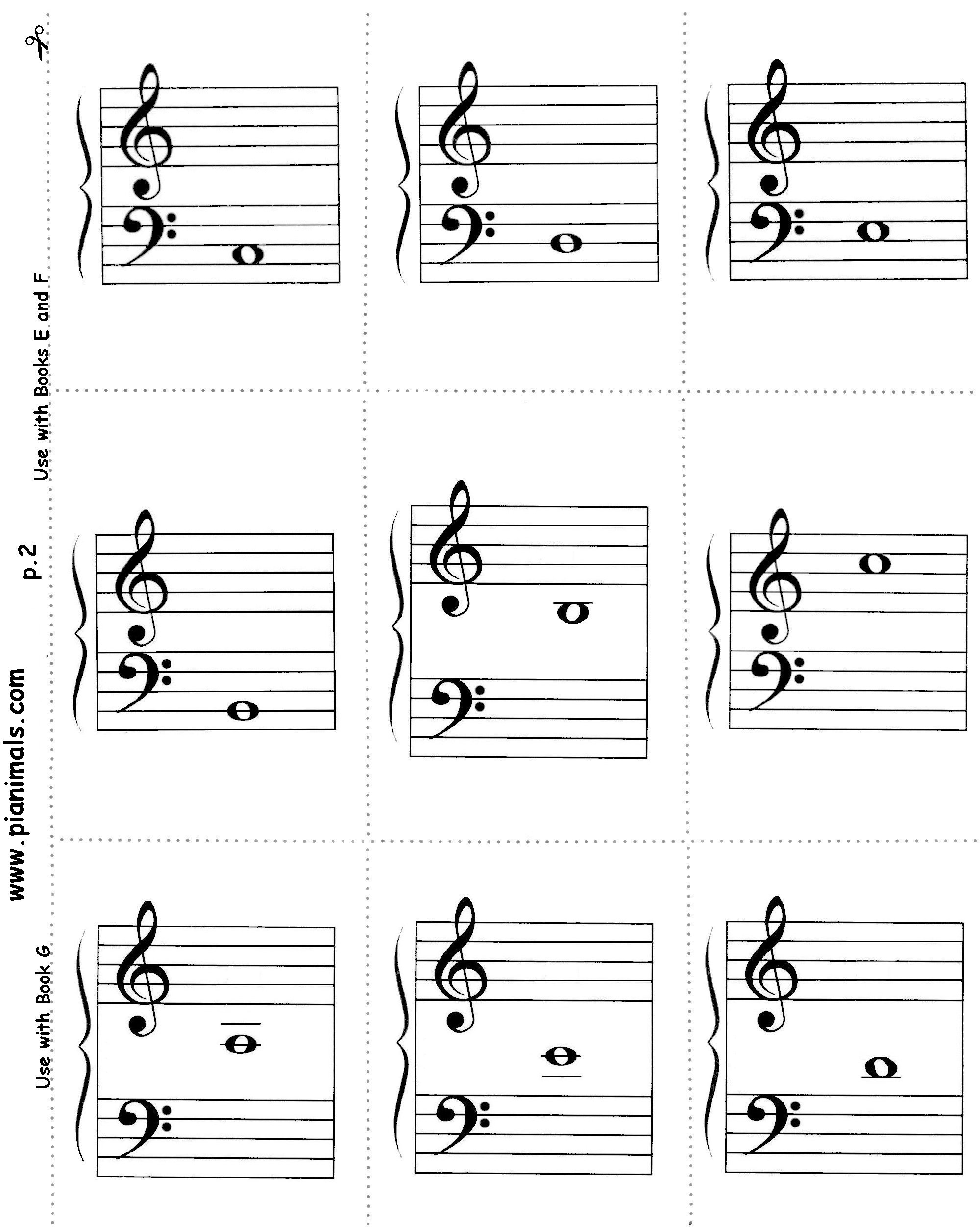
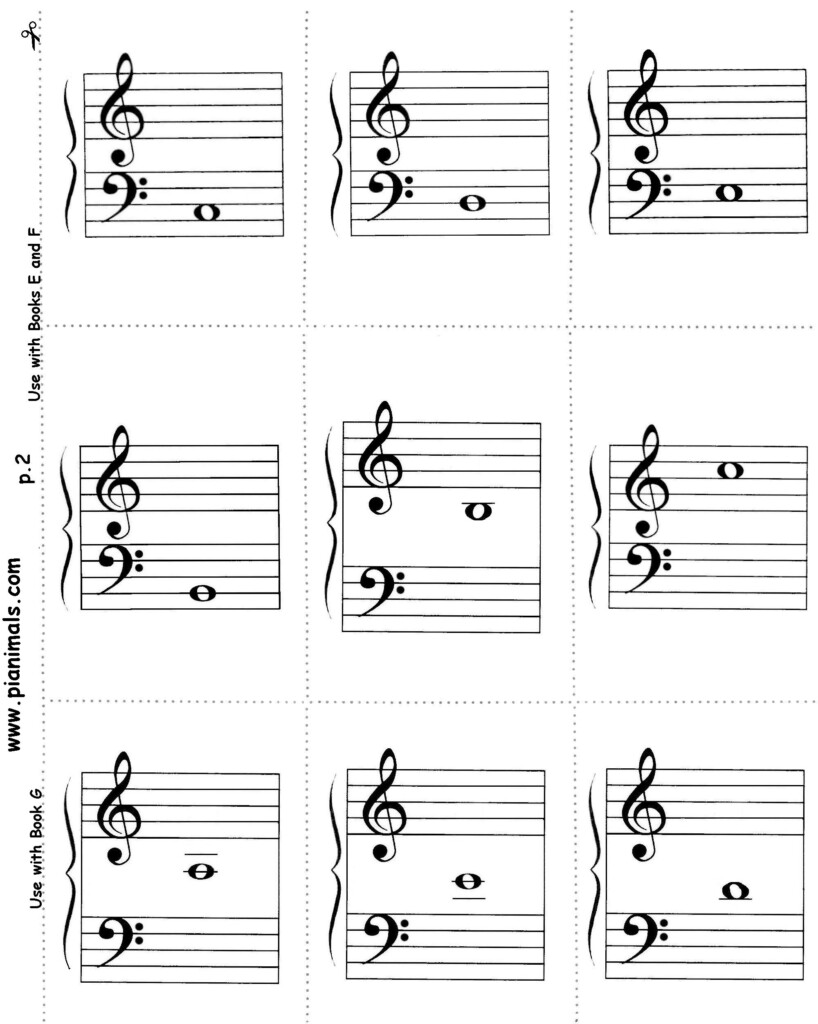
Free Printable Music Flashcards – Sheet music refers to the handwritten or printed form of musical notation. It uses musical symbolisms to represent the rhythms, notes, or chords in a piece. The majority of sheet music can be printed onto paper. It is a valuable source for musicians and a popular way for people to learn to play musical instruments.
It is possible to find printed music in various styles. It is perfect for students of all ages and stages. These materials are hand-crafted by artists who are self-employed. When you purchase these products, you are helping to bring money back into the pockets of artists who are independent. You can print music to create an enjoyable learning environment for your children.
The very first sheet music printed wasn’t available for download. Some publishers began to offer printed sheets for promotion purposes. These first publications were a collection of songs as well as catalogs and melodies. Publishers began printing whole pages of music later. To promote their products, some companies issued sheets of music. To ensure that they did not violate these licenses, publishers had to give credit.
The first music book printed was called the Mainz Psalter. The baroque period saw composers using moving type to make notes and musical marks. This period saw many composers use the figured bass. These techniques were made possible by the printing press. The printed copy of this work is in numerous libraries.
Printing a music sheet is an easy process, but there are several essential things to bear in your mind. The first step is obtaining the appropriate print license. A typical print license is valid for up to five consecutive years. Inventory that is not used can be sold off over the duration of the agreement for six to twelve month. This use will be subject to a charge from the music publisher. You will then have to decide how to distribute these printed sheet music.
Printing music was not easy prior to the printing press was invented. It took many centuries for printing to become an everyday process. The method of using moving type to print music was difficult until the invention of printing presses helped make the process simpler. Petrucci developed the triple-impression technique, which allowed Petrucci to print the words, staff lines and notes in three separate impressions. This method was later used to print music.
Music printing has made it easier for professional and amateur musicians alike to have access to music. It also made it simpler for amateur musicians to compose music. Music industry also gained from this shift. Composers could now create more music for amateur musicians. This increased the popularity of secular music.
When it comes to music, there are a variety of factors to consider before purchasing sheet music. First, it is important that the pieces or scores are simple to read. They must also be simple to read on a music stand. The binding style is a different factor to take into consideration. It can be difficult to remove a music part or score when it’s bound on thick paper. You should therefore buy a thin, flat sheet that will lay flat on a musical stand.
The speed of the music is another aspect to take into consideration when choosing the music score. In the case of the piece that it’s composed for, the composer might request that the performer play a particular section of the music. The composer may mention this in the sheet music to communicate the intention to the listeners. The sign for repeat is usually identified by two dots at the end of the section. The repeat can be a complete section or a single bar. You may also select various types of repeat.
Partbooks were common in the Renaissance period to produce polyphonic works that were multi-part. In a madrigal that had multiple parts such as a madrigal, for instance parts of the madrigal would be published in a separate book. Partbooks were used by instrumentalists as well as singers. Scores of multi-part music were rarely printed during the period. Josquin des Prez, however, is credited for using the score format.
A different form of the common score. It’s the simplified version of a full orchestral score. It is the norm when orchestral works are being composed. Short scores are usually not published, however they can be employed for rehearsals or studying.